SeString
The game uses a custom null-terminated string implementation, which allows strings to carry binary payloads.
The name SeString was invented at the time of its discovery and has been in use in the plugin development community ever since. At some point RTTI data was embedded into the exe and since then we know the class implementing them is actually called Utf8String.
Internally, the game has a MacroEncoder to convert a string representation of the binary payload (what we call macro string) to binary data, and a MacroDecoder, which can decode binary payloads to execute whatever the macro specific implementation should do.
This guide will use the most up-to-date C# implementation to parse and create
SeStrings, which is Luminas ReadOnlySeString
or ReadOnlySeStringSpan
and the SeStringBuilder.
The class Lumina.Text.SeString is an old implementation and should no longer
be used.
The same applies to the Dalamuds SeString and SeStringBuilder classes, but since
many Dalamuds APIs still require Dalamuds SeString type, you can convert
Lumina.Text.ReadOnly.ReadOnlySeString and
Lumina.Text.ReadOnly.ReadOnlySeStringSpan to
Dalamud.Game.Text.SeStringHandling.SeString using the ToDalamudString()
extensions
found in the Dalamud.Utility namespace.
Dalamuds SeString class is missing a lot of payloads types, has incorrect payload/macro names, and has no support for expressions as explained in this guide.
ReadOnlySeString is an owning type that manages the underlying data buffer. In
contrast, ReadOnlySeStringSpan is a lightweight, non-owning view, useful for
scenarios like parsing a SeString from a raw pointer without taking ownership.
Payloads
Payloads have several use cases, such as changing the text color, play chat
sound effects, add interactable links, add logic to them with if and switch
macros and they can even be used to fill in local or global parameters (like the
players name or the current time).
Each payload has the following structure:
- start byte (
0x02) - macro code (1 byte)
- length of the macro (integer expression)
- macro-specific expressions
- end byte (
0x03)
Let's see it in action by writing text in bold letters.
To demonstrate this, we're going to use the SeString Creator widget that can be
found in /xldata. It allows us to experiment with macro strings, preview and
inspect the evaluated result.
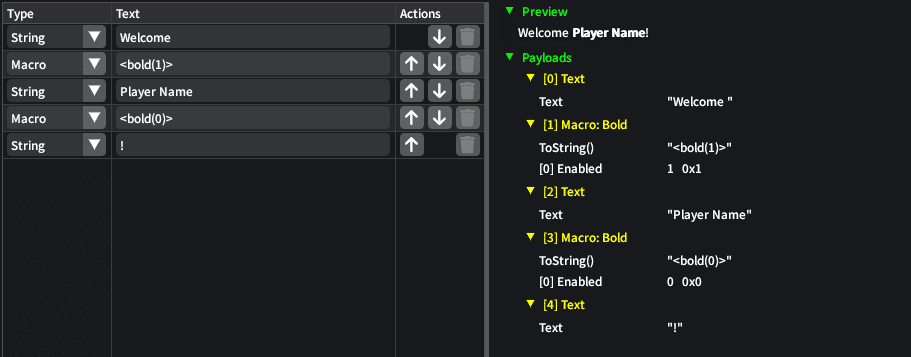
The macro string <bold(1)> enables bold text, and <bold(0)> disables bold
text.
In binary form, this would look like this:
0x57, 0x65, 0x6C, 0x63, 0x6F, 0x6D, 0x65, 0x20, // Text "Welcome "
0x02, // Payload start
0x19, // Macro code for bold
0x02, // Integer expression for the payload length (1)
0x02, // Integer expression for the enable state (on)
0x03, // Payload end
0x50, 0x6C, 0x61, 0x79, 0x65, 0x72, 0x20, 0x4E, 0x61, 0x6D, 0x65, // Text "Player Name"
0x02, // Payload start
0x19, // Macro code for bold
0x02, // Integer expression for the payload length (1)
0x01, // Integer expression for the enable state (off)
0x03, // Payload end
0x21 // Text "!"
This can be done programmatically:
- Variant 1
- Variant 2
- Variant 3
var example = new SeStringBuilder()
.Append("Welcome ")
.BeginMacro(MacroCode.Bold)
.AppendIntExpression(1)
.EndMacro()
.Append("Player Name")
.BeginMacro(MacroCode.Bold)
.AppendIntExpression(0)
.EndMacro()
.Append("!")
.ToReadOnlySeString();
var example = new SeStringBuilder()
.Append("Welcome ")
.AppendSetBold(true)
.Append("Player Name")
.AppendSetBold(false)
.Append("!")
.ToReadOnlySeString();
var example = new SeStringBuilder()
.Append("Welcome ")
.AppendBold("Player Name")
.Append("!")
.ToReadOnlySeString();
But before we get to macros, let's have a look at expressions first.
Expressions
There are several types of expressions and they are identified by the value range in the first byte.
Integer Expressions
If the first and only byte is > 0 and < 0xD0, it's as simple as subtracting
1 from the byte for the actual integer value.
This is done to avoid byte 0x00, which would be intepreted as null-terminator.
Whether the value is used as unsigned or signed integer depends on the
implementation of the macro parsing it.
Example <num(3)>:
- Binary Form
- Code
0x02, // Payload start
0x20, // Macro code for num
0x02, // Integer expression for the payload length (1)
0x04, // Integer expression for the value (3)
0x03 // Payload end
var example = new SeStringBuilder()
.BeginMacro(MacroCode.Num)
.AppendIntExpression(3)
.EndMacro()
.ToReadOnlySeString();
If the first byte is >= 0xF0 and <= 0xFE, the integer expression is of variable length. The number of bytes to read is encoded in the lower 4 bits of the type byte. See SeExpressionUtilities.TryDecodeUInt for more details.
Example <num(300000)>:
- Binary Form
- Code
0x02, // Payload start
0x20, // Macro code for num
0x05, // Integer expression for the payload length (4)
0xF6, // Integer expression for the value
0x04, 0x93, 0xE0, // 0x0493E0 = 300000
0x03 // Payload end
var example = new SeStringBuilder()
.BeginMacro(MacroCode.Num)
.AppendIntExpression(300000)
.EndMacro()
.ToReadOnlySeString();
Placeholder Expressions
Between the integer expression types, placeholder expressions snuck in.
If the type byte is >= 0xD0 and <= 0xDF or 0xEC, the following placeholders
are used:
| Type Byte | Macro String | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 0xD8 | t_msec | Uses the millisecond value in the contextual time storage. |
| 0xD9 | t_sec | Uses the second value in the contextual time storage. |
| 0xDA | t_min | Uses the minute value in the contextual time storage. |
| 0xDB | t_hour | Uses the hour value in the contextual time storage, ranging from 0 to 23. |
| 0xDC | t_day | Uses the day of month value in the contextual time storage. |
| 0xDD | t_wday | Uses the weekday value in the contextual time storage, ranging from 1 (Sunday) to 7 (Saturday). |
| 0xDE | t_mon | Uses the month value in the contextual time storage, ranging from 0 (January) to 11 (December). |
| 0xDF | t_year | Uses the year value in the contextual time storage, where 0 means the year 1900. |
| 0xEC | stackcolor | Uses the last color value pushed. |
Placeholder types 0xD0 to 0xD7 are currently unknown.
Time-related placeholders can use the time set via the settime or
setresettime macros.
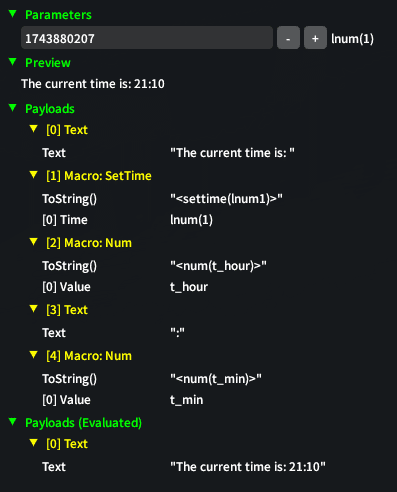
Example The current time is: <settime(1743880207)><num(t_hour)>:<num(t_min)>
(The current time is: 21:10):
- Binary Form
- Code
0x54, 0x68, 0x65, 0x20, 0x63, 0x75, 0x72, 0x72, 0x65, 0x6E, 0x74, 0x20, 0x74, 0x69, 0x6D, 0x65, 0x20, 0x69, 0x73, 0x3A, 0x20, // Text "The current time is: "
0x02, // Payload start
0x07, // Macro code for settime
0x06, // Integer expression for the payload length (5)
0xFE, 0x67, 0xF1, 0x80, 0x0F, // Integer expression for the timestamp (1743880207)
0x03, // Payload end
0x02, // Payload start
0x20, // Macro code for num
0x02, // Integer expression for the payload length (1)
0xDB, // Placeholder expression for t_hour
0x03, // Payload end
0x3A,
0x02, // Payload start
0x20, // Macro code for num
0x02, // Integer expression for the payload length (1)
0xDA, // Placeholder expression for t_min
0x03 // Payload end
var example = new SeStringBuilder()
.Append("The current time is: ")
.BeginMacro(MacroCode.SetTime)
.AppendIntExpression(1743880207)
.EndMacro()
.BeginMacro(MacroCode.Num)
.AppendNullaryExpression(ExpressionType.Hour)
.EndMacro()
.Append(":")
.BeginMacro(MacroCode.Num)
.AppendNullaryExpression(ExpressionType.Minute)
.EndMacro()
.ToReadOnlySeString();
Binary Expressions
If the type byte is >= 0xE0 and <= 0xE5, the following comparison and equality operators are used:
| Type Byte | Macro String | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 0xE0 | [val1>=val2] | Tests if the evaluated result from first sub-expression is greater than or equal to the evaluated result from second sub-expression. |
| 0xE1 | [val1>val2] | Tests if the evaluated result from first sub-expression is greater than the evaluated result from second sub-expression. |
| 0xE2 | [val1<=val2] | Tests if the evaluated result from first sub-expression is less than or equal to the evaluated result from second sub-expression. |
| 0xE3 | [val1<val2] | Tests if the evaluated result from first sub-expression is less than the evaluated result from second sub-expression. |
| 0xE4 | [val1==val2] | Tests if the evaluated result from first sub-expression is equal to the evaluated result from second sub-expression. |
| 0xE5 | [val1!=val2] | Tests if the evaluated result from first sub-expression is not equal to the evaluated result from second sub-expression. |
The type byte is followed by 2 expressions for each of the operands.
Example 1 == 1 = <if([1==1],true,false)>:
- Binary Form
- Code
0x31, 0x20, 0x3D, 0x3D, 0x20, 0x31, 0x20, 0x3D, 0x20, // Text "1 == 1 = "
0x02, // Payload start
0x08, // Macro code for if
0x11, // Integer expression for the payload length (16)
0xE4, // Binary expression for equality check
0x02, // Integer expression for the first value (1)
0x02, // Integer expression for the second value (1)
0xFF, 0x05, 0x74, 0x72, 0x75, 0x65, // String expression used when condition is true (Text "true")
0xFF, 0x06, 0x66, 0x61, 0x6C, 0x73, 0x65, // String expression used when condition is false (Text "false")
0x03 // Payload end
var example = new SeStringBuilder()
.Append("1 == 1 = ")
.BeginMacro(MacroCode.If)
.BeginBinaryExpression(ExpressionType.Equal)
.AppendIntExpression(1)
.AppendIntExpression(1)
.EndExpression()
.AppendStringExpression("true")
.AppendStringExpression("false")
.EndMacro()
.ToReadOnlySeString();
Parameter Expressions
If the type byte is >= 0xE8 and <= 0xEB, the following parameters are used:
| Type Byte | Macro String | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 0xE8 | lnum# | Uses a numeric value at the specified index in the local parameter storage. |
| 0xE9 | gnum# | Uses a numeric value at the specified index in the global parameter storage. |
| 0xEA | lstr# | Uses a SeString value at the specified index in the local parameter storage. |
| 0xEB | gstr# | Uses a SeString value at the specified index in the global parameter storage. |
Following the type byte is a byte indicating the index of the parameter. The first index is 1.
Local Parameters
Local parameters have to be passed to the evaluator function. See Evaluating SeStrings below.
Global Parameters
Global parameters are stored and automatically resolved in the games MacroDecoder (note that the index for the StdDeque GlobalParameters in the MacroDecoder starts at 0).
Expand for a list of the currently known global parameters
| Index | Type | Label |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | String | Player Name |
| 2 | String | Temp Entity 1: Name |
| 3 | String | Temp Entity 2: Name |
| 4 | Integer | Player Sex |
| 5 | Integer | Temp Entity 1: Sex |
| 6 | Integer | Temp Entity 2: Sex |
| 7 | Integer | Temp Entity 1: ObjStrId |
| 8 | Integer | Temp Entity 2: ObjStrId |
| 11 | Integer | Eorzea Time Hours |
| 12 | Integer | Eorzea Time Minutes |
| 13 | Integer | ConfigOption ColorSay |
| 14 | Integer | ConfigOption ColorShout |
| 15 | Integer | ConfigOption ColorTell |
| 16 | Integer | ConfigOption ColorParty |
| 17 | Integer | ConfigOption ColorAlliance |
| 18 | Integer | ConfigOption ColorLS1 |
| 19 | Integer | ConfigOption ColorLS2 |
| 20 | Integer | ConfigOption ColorLS3 |
| 21 | Integer | ConfigOption ColorLS4 |
| 22 | Integer | ConfigOption ColorLS5 |
| 23 | Integer | ConfigOption ColorLS6 |
| 24 | Integer | ConfigOption ColorLS7 |
| 25 | Integer | ConfigOption ColorLS8 |
| 26 | Integer | ConfigOption ColorFCompany |
| 27 | Integer | ConfigOption ColorPvPGroup |
| 28 | Integer | ConfigOption ColorPvPGroupAnnounce |
| 29 | Integer | ConfigOption ColorBeginner |
| 30 | Integer | ConfigOption ColorEmoteUser |
| 31 | Integer | ConfigOption ColorEmote |
| 32 | Integer | ConfigOption ColorYell |
| 33 | Integer | ConfigOption ColorFCAnnounce |
| 34 | Integer | ConfigOption ColorBeginnerAnnounce |
| 35 | Integer | ConfigOption ColorCWLS |
| 36 | Integer | ConfigOption ColorAttackSuccess |
| 37 | Integer | ConfigOption ColorAttackFailure |
| 38 | Integer | ConfigOption ColorAction |
| 39 | Integer | ConfigOption ColorItem |
| 40 | Integer | ConfigOption ColorCureGive |
| 41 | Integer | ConfigOption ColorBuffGive |
| 42 | Integer | ConfigOption ColorDebuffGive |
| 43 | Integer | ConfigOption ColorEcho |
| 44 | Integer | ConfigOption ColorSysMsg |
| 52 | Integer | Player Grand Company Rank (Maelstrom) |
| 53 | Integer | Player Grand Company Rank (Twin Adders) |
| 54 | Integer | Player Grand Company Rank (Immortal Flames) |
| 55 | String | Companion Name |
| 56 | String | Content Name |
| 57 | Integer | ConfigOption ColorSysBattle |
| 58 | Integer | ConfigOption ColorSysGathering |
| 59 | Integer | ConfigOption ColorSysErr |
| 60 | Integer | ConfigOption ColorNpcSay |
| 61 | Integer | ConfigOption ColorItemNotice |
| 62 | Integer | ConfigOption ColorGrowup |
| 63 | Integer | ConfigOption ColorLoot |
| 64 | Integer | ConfigOption ColorCraft |
| 65 | Integer | ConfigOption ColorGathering |
| 66 | Integer | Temp Entity 1: Name starts with Vowel |
| 67 | Integer | Temp Entity 2: Name starts with Vowel |
| 68 | Integer | Player ClassJobId |
| 69 | Integer | Player Level |
| 70 | Integer | Player StartTown |
| 71 | Integer | Player Race |
| 72 | Integer | Player Synced Level |
| 74 | Integer | Quest#66047: Has met Alphinaud and Alisaie |
| 75 | Integer | PlayStation Generation |
| 76 | Integer | Is Legacy Player |
| 78 | Integer | Client/Platform? |
| 79 | Integer | Player BirthMonth |
| 80 | Integer | ConfigOption PadMode |
| 83 | Integer | Datacenter Region |
| 84 | Integer | ConfigOption ColorCWLS2 |
| 85 | Integer | ConfigOption ColorCWLS3 |
| 86 | Integer | ConfigOption ColorCWLS4 |
| 87 | Integer | ConfigOption ColorCWLS5 |
| 88 | Integer | ConfigOption ColorCWLS6 |
| 89 | Integer | ConfigOption ColorCWLS7 |
| 90 | Integer | ConfigOption ColorCWLS8 |
| 92 | Integer | Player Grand Company |
| 93 | Integer | TerritoryType Id |
| 94 | Integer | Is Soft Keyboard Enabled |
| 95 | Integer | ConfigOption LogColorRoleTank for LogSetRoleColor 1 |
| 96 | Integer | ConfigOption LogColorRoleTank for LogSetRoleColor 2 |
| 97 | Integer | ConfigOption LogColorRoleHealer for LogSetRoleColor 1 |
| 98 | Integer | ConfigOption LogColorRoleHealer for LogSetRoleColor 2 |
| 99 | Integer | ConfigOption LogColorRoleDPS for LogSetRoleColor 1 |
| 100 | Integer | ConfigOption LogColorRoleDPS for LogSetRoleColor 2 |
| 101 | Integer | ConfigOption LogColorOtherClass for LogSetRoleColor 1 |
| 102 | Integer | ConfigOption LogColorOtherClass for LogSetRoleColor 2 |
| 103 | Integer | Has Login Security Token |
| 104 | Integer | Is subscribed to PlayStation Plus |
| 105 | Integer | ConfigOption PadMouseMode |
| 107 | Integer | Preferred World Bonus Max Level |
| 108 | Integer | Occult Crescent Support Job Level |
| 109 | Integer | Deep Dungeon Id |
String Expressions
If the type byte is 0xFF, this is a String expression. It's followed by an integer expression for its length and the nested SeString.
Example Hello <split(<string(gstr1)>, ,1)>!:
- Binary Form
- Code
0x48, 0x65, 0x6C, 0x6C, 0x6F, 0x20, // Text "Hello "
0x02, // Payload start
0x2C, // Macro code for split
0x0D, // Integer expression for the payload length (12)
0xFF, // String expression for the input
0x07, // Integer expression for the length of the following string (6)
0x02, // Payload start
0x29, // Macro code for string
0x03, // Integer expression for the payload length (2)
0xEB, // Parameter expression gstr
0x02, // Integer expression for gstr1 (local player name)
0x03, // Payload end
0xFF, // String expression for the separator
0x02, // Integer expression for the length of the following string (1)
0x20, // Text " "
0x02, // Integer expression for the index (1) of the splitted text (in this case the forename of a local player)
0x03, // Payload end
0x21 // Text "!"
var example = new SeStringBuilder()
.Append("Hello ")
.BeginMacro(MacroCode.Split)
.AppendStringExpression(new SeStringBuilder() // input
.BeginMacro(MacroCode.String)
.AppendGlobalStringExpression(1) // gstr1
.EndMacro()
.ToReadOnlySeString().AsSpan())
.AppendStringExpression(" ") // separator
.AppendIntExpression(1) // index of the splitted text
.EndMacro()
.Append("!")
.ToReadOnlySeString();
See SeExpressionUtilities.TryDecodeString for more details.
Now that we have expressions covered, let's see what we can do with them!
Macros
Macro payloads work kind of like functions: each one performs a specific action, and the expressions attached to them are like the parameters you pass in.
[0x06] SetResetTime
Sets the reset time to the contextual time storage.
Expressions:
- [0] Integer Expression: Hour (in Japan Standard Time)
- [1] Integer Expression: Weekday (0-6 = Sunday to Saturday, 7 = Special case for daily resets)
Can be evaluated using ISeStringEvaluator (code).
Example
<setresettime(17,2)>
→ Sets the contextual time to next Tuesday, 8 am UTC.
var example = new SeStringBuilder()
.BeginMacro(MacroCode.SetResetTime)
.AppendIntExpression(17)
.AppendIntExpression(2)
.EndMacro()
.BeginMacro(MacroCode.Sec)
.AppendNullaryExpression(ExpressionType.Day)
.EndMacro()
.Append(".")
.BeginMacro(MacroCode.Sec)
.AppendNullaryExpression(ExpressionType.Month)
.EndMacro()
.Append(". at ")
.BeginMacro(MacroCode.Sec)
.AppendNullaryExpression(ExpressionType.Hour)
.EndMacro()
.Append(":")
.BeginMacro(MacroCode.Sec)
.AppendNullaryExpression(ExpressionType.Minute)
.EndMacro()
.ToReadOnlySeString();
var result = SeStringEvaluator.Evaluate(example);
→ Prints 03.03. at 09:00 (at time of writing, in UTC+1).
[0x07] SetTime
Sets the specified time to the contextual time storage.
Expressions:
- [0] Integer Expression: Unix Timestamp
Can be evaluated using ISeStringEvaluator (code).
Example
<settime(1743880207)>
→ Sets the contextual time to Sat Apr 05 2025 19:10:07 UTC.
var example = new SeStringBuilder()
.BeginMacro(MacroCode.SetTime)
.AppendIntExpression(1743880207)
.EndMacro()
.BeginMacro(MacroCode.Num)
.AppendNullaryExpression(ExpressionType.Hour)
.EndMacro()
.Append(":")
.BeginMacro(MacroCode.Num)
.AppendNullaryExpression(ExpressionType.Minute)
.EndMacro()
.ToReadOnlySeString();
var result = SeStringEvaluator.Evaluate(example);
- Prints
21:10.
[0x08] If
Tests an expression and uses a corresponding subexpression.
Expressions:
- [0] Expression used as condition
- [1] Expression to use if condition is true
- [2] Expression to use if condition is false
Can be evaluated using ISeStringEvaluator (code).
Example
Good <if([gnum11<12],<if([gnum11<4],evening,morning)>,<if([gnum11<17],day to you,evening)>)>, friend.
→ Between 4 am and 12 pm Eorzea Time, this will print Good morning, friend.
→ Between 12 pm and 5 pm Eorzea Time, this will print
Good day to you, friend.
→ Between 5 pm and 4 am Eorzea Time, this will print Good evening, friend.
var example = new SeStringBuilder()
.Append("Good ")
.BeginMacro(MacroCode.If)
.BeginBinaryExpression(ExpressionType.LessThan)
.AppendGlobalNumberExpression(11)
.AppendIntExpression(12)
.EndExpression()
.BeginStringExpression()
.BeginMacro(MacroCode.If)
.BeginBinaryExpression(ExpressionType.LessThan)
.AppendGlobalNumberExpression(11)
.AppendIntExpression(4)
.EndExpression()
.AppendStringExpression("evening")
.AppendStringExpression("morning")
.EndMacro()
.EndExpression()
.BeginStringExpression()
.BeginMacro(MacroCode.If)
.BeginBinaryExpression(ExpressionType.LessThan)
.AppendGlobalNumberExpression(11)
.AppendIntExpression(17)
.EndExpression()
.AppendStringExpression("day to you")
.AppendStringExpression("evening")
.EndMacro()
.EndExpression()
.EndMacro()
.Append(", friend.")
.ToReadOnlySeString();
var result = SeStringEvaluator.Evaluate(example);
[0x09] Switch
Tests an expression and uses a corresponding subexpression.
Expressions:
- [0] Expression used as condition
- [1] Expression to use if condition is 1
- ...
- [n] Expression to use if condition is n
Can be evaluated using ISeStringEvaluator (code).
Example
<switch(lnum1,S,M,L,XL)>
→ Prints S when lnum1 is 1.
→ Prints M when lnum1 is 2.
→ Prints L when lnum1 is 3.
→ Prints XL when lnum1 is 4.
var example = new SeStringBuilder()
.BeginMacro(MacroCode.Switch)
.AppendLocalNumberExpression(1)
.AppendStringExpression("S")
.AppendStringExpression("M")
.AppendStringExpression("L")
.AppendStringExpression("XL")
.EndMacro()
.ToReadOnlySeString();
var result = SeStringEvaluator.Evaluate(example, [2]);
- Prints
M.
[0x0A] PcName
Adds a characters name.
Expressions:
- [0] Integer Expression: EntityId
Can be evaluated using ISeStringEvaluator (code).
Example
<pcname(0x10778681)>
→ Prints the name of the player character with EntityId 0x10778681.
var example = new SeStringBuilder()
.BeginMacro(MacroCode.PcName)
.AppendIntExpression(0x10778681)
.EndMacro()
.ToReadOnlySeString();
var result = SeStringEvaluator.Evaluate(example);
[0x0B] IfPcGender
Tests a characters gender.
Expressions:
- [0] Integer Expression: EntityId
- [1] Expression to use if the character is male
- [2] Expression to use if the character is female
Can be evaluated using ISeStringEvaluator (code).
Example
Good day, <ifpcgender(0x10778681,Sir,Ma'am)>.
→ Prints Good day, Sir. if the player character with EntityId 0x10778681 is
male.
→ Prints Good day, Ma'am. if the player character with EntityId 0x10778681 is
female.
var example = new SeStringBuilder()
.Append("Good day, ")
.BeginMacro(MacroCode.IfPcGender)
.AppendIntExpression(0x10778681)
.AppendStringExpression("Sir")
.AppendStringExpression("Ma'am")
.EndMacro()
.Append(".")
.ToReadOnlySeString();
var result = SeStringEvaluator.Evaluate(example);
[0x0C] IfPcName
Tests a characters name.
Expressions:
- [0] Integer Expression: EntityId
- [1] String Expression: The name to test against
- [2] Expression to use if the name matches
- [3] Expression to use if the name doesn't match
Can be evaluated using ISeStringEvaluator (code).
Example
Hello, <ifpcname(0x10778681,Local Player,Warrior of Light,adventurer)>!
→ Prints Hello, Warrior of Light! if the player character with EntityId
0x10778681 is called Local Player.
→ Prints Hello, adventurer! if the player character with EntityId 0x10778681
is not called Local Player.
var example = new SeStringBuilder()
.Append("Hello, ")
.BeginMacro(MacroCode.IfPcName)
.AppendIntExpression(0x10778681)
.AppendStringExpression("Local Player")
.AppendStringExpression("Warrior of Light")
.AppendStringExpression("adventurer")
.EndMacro()
.Append("!")
.ToReadOnlySeString();
var result = SeStringEvaluator.Evaluate(example);
[0x0D] Josa
Determines the type of josa required from the last character of the first expression.
Expressions:
- [0] test string
- [1] eun/i/eul suffix
- [2] neun/ga/reul suffix
[0x0E] Josaro
Determines the type of josa, ro in particular, required from the last character of the first expression.
Expressions:
- [0] test string
- [1] ro suffix
- [2] euro suffix
[0x0F] IfSelf
Tests if the character is the local player.
Expressions:
- [0] Integer Expression: EntityId
- [1] Expression to use if the character is the local player
- [2] Expression to use if the character is not the local player
Can be evaluated using ISeStringEvaluator (code).
Example
<ifself(0x10778681,You are,<pcname(0x10778681)> is)> KO'd.
→ Prints You are KO'd. if the player character with EntityId 0x10778681 is the
Local Player.
→ Prints Other Player is KO'd. if the player character with EntityId
0x10778681 is not the Local Player, called Other Player.
var example = new SeStringBuilder()
.BeginMacro(MacroCode.IfSelf)
.AppendIntExpression(0x10778681)
.AppendStringExpression("You are")
.BeginStringExpression()
.BeginMacro(MacroCode.PcName)
.AppendIntExpression(0x10778681)
.EndMacro()
.Append(" is")
.EndExpression()
.EndMacro()
.Append(" KO'd.")
.ToReadOnlySeString();
var result = SeStringEvaluator.Evaluate(example);
[0x10] NewLine
Adds a line break.
No expressions.
This macro is used for formatting. It is not evaluated by ISeStringEvaluator.
Example
Hello<br>World
→ Prints
Hello
World
var example = new SeStringBuilder()
.Append("Hello")
.AppendNewLine()
.Append("World")
.ToReadOnlySeString();
or
var example = new SeStringBuilder()
.AppendLine("Hello")
.Append("World")
.ToReadOnlySeString();
[0x11] Wait
Waits for a specified duration.
Expressions:
- [0] Integer Expression: Delay in seconds
[0x12] Icon
Adds an icon from common/font/gfdata.gfd. See
BitmapFontIcon
enum for details.
Expressions:
- [0] Integer Expression: Icon ID
This does not support icons from ui/icon/.
Expand for a list available icons (as of Patch )
| Id | Icon |
|---|---|
| 1 | |
| 2 | |
| 3 | |
| 4 | |
| 5 | |
| 6 | |
| 7 | |
| 8 | |
| 9 | |
| 10 | |
| 11 | |
| 12 | |
| 13 | |
| 14 | |
| 15 | |
| 16 | |
| 17 | |
| 18 | |
| 19 | |
| 20 | |
| 21 | |
| 22 | |
| 23 | |
| 24 | |
| 25 | |
| 51 | |
| 52 | |
| 53 | |
| 54 | |
| 55 | |
| 56 | |
| 57 | |
| 58 | |
| 59 | |
| 60 | |
| 61 | |
| 62 | |
| 63 | |
| 64 | |
| 65 | |
| 66 | |
| 67 | |
| 68 | |
| 70 | |
| 71 | |
| 72 | |
| 73 | |
| 74 | |
| 75 | |
| 76 | |
| 77 | |
| 78 | |
| 79 | |
| 80 | |
| 81 | |
| 82 | |
| 83 | |
| 84 | |
| 85 | |
| 86 | |
| 87 | |
| 88 | |
| 89 | |
| 90 | |
| 91 | |
| 92 | |
| 93 | |
| 94 | |
| 95 | |
| 96 | |
| 97 | |
| 98 | |
| 99 | |
| 100 | |
| 101 | |
| 102 | |
| 103 | |
| 104 | |
| 105 | |
| 106 | |
| 107 | |
| 108 | |
| 109 | |
| 110 | |
| 111 | |
| 112 | |
| 113 | |
| 114 | |
| 115 | |
| 116 | |
| 117 | |
| 118 | |
| 119 | |
| 120 | |
| 121 | |
| 122 | |
| 124 | |
| 125 | |
| 126 | |
| 127 | |
| 128 | |
| 129 | |
| 130 | |
| 131 | |
| 132 | |
| 133 | |
| 134 | |
| 135 | |
| 136 | |
| 137 | |
| 138 | |
| 139 | |
| 140 | |
| 141 | |
| 142 | |
| 143 | |
| 144 | |
| 145 | |
| 146 | |
| 147 | |
| 148 | |
| 149 | |
| 150 | |
| 151 | |
| 152 | |
| 153 | |
| 154 | |
| 155 | |
| 156 | |
| 157 | |
| 158 | |
| 159 | |
| 160 | |
| 161 | |
| 162 | |
| 163 | |
| 164 | |
| 165 | |
| 166 | |
| 167 | |
| 168 | |
| 169 | |
| 170 | |
| 171 | |
| 172 | |
| 173 | |
| 174 | |
| 175 | |
| 176 | |
| 177 | |
| 178 | |
| 179 | |
| 180 | |
| 181 |
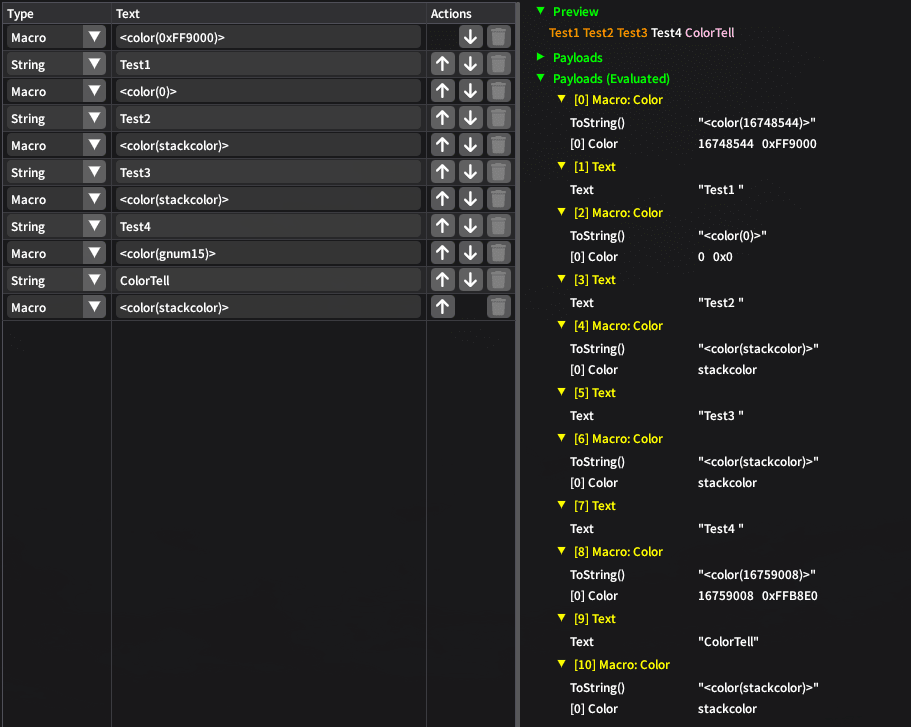
[0x13] Color
Pushes the text foreground color.
Expressions:
- [0] An expression resolving to a B8G8R8A8 color, or Placeholder Expression
stackcolor- If a color was passed, it pushes it onto the stack, similar to
ImGui.PushStyleColor(ImGuiCol.Text, color). - If 0 is passed, it re-uses the current color on the stack, similar to
ImGui.PushStyleColor(ImGuiCol.Text, ImGui.GetColorU32(ImGuiCol.Text)). - If
stackcolorwas passed, the color is popped from the stack, similar toImGui.PopStyleColor().
- If a color was passed, it pushes it onto the stack, similar to
The expression can be evaluated using ISeStringEvaluator (code).
Always make sure that when you push a color, it is popped from the stack with
stackcolor! The ImGui renderer might be forgiving, but the game is not.
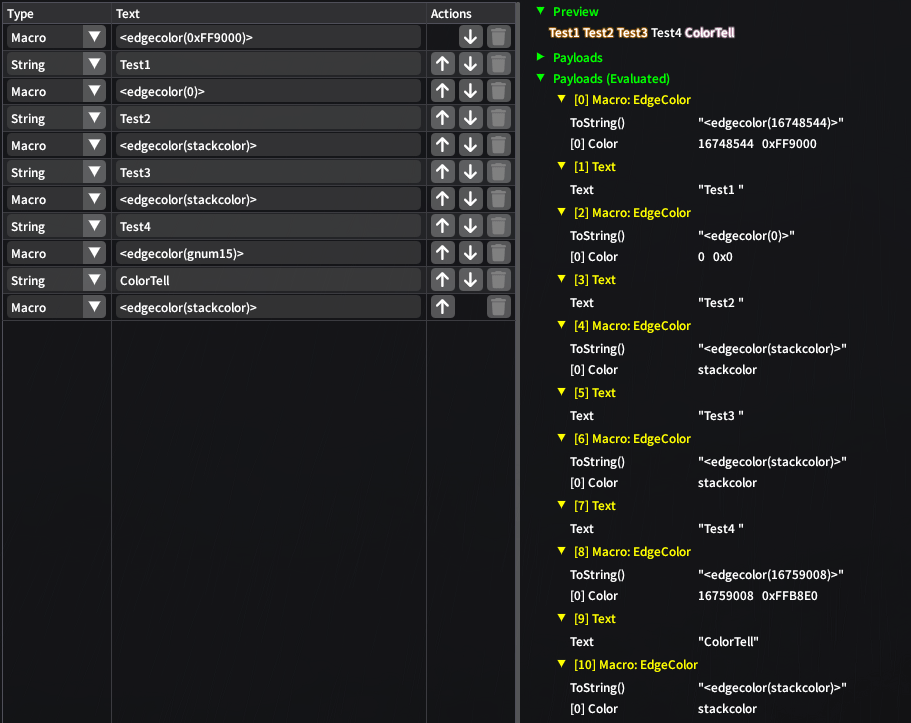
[0x14] EdgeColor
Pushes the text border color.
See Color macro for expression description.
The expression can be evaluated using ISeStringEvaluator (code).
Always make sure that when you push an edgecolor, it is popped from the stack
with stackcolor!
[0x15] ShadowColor
Pushes the text shadow color.
See Color macro for expression description.
The expression can be evaluated using ISeStringEvaluator (code).
[0x16] SoftHyphen
Adds a soft hyphen.
No expressions.
Macro string: <->
→ Invisible soft hyphen \u00AD.
Localized text pulled from the game's Excel sheets, specifically French and
German texts, will almost certainly contain soft hyphens (represented in macro
strings as <->). Soft hyphens indicate potential word break points at
syllables. They are normally invisible and only appear at the end of a line when
a word needs to be broken. In this case, they render as a visible - to mark the
split. However ImGui (for example, ImGui.Text()) doesn't handle this correctly
and will always display soft hyphens, even if no line break occurs.
If you notice soft hyphens are being displayed, you can remove them from a
string using the
StripSoftHyphen()
extension provided by Dalamud.
[0x17] Key
Unknown purpose.
[0x18] Scale
Unknown purpose.
[0x19] Bold
Sets whether to use bold text effect.
- [0] An expression resolving to a boolean for the enable state. 0 = off, 1 = on
The expression can be evaluated using ISeStringEvaluator (code).
The chat log does not support bold text.
[0x1A] Italic
Sets whether to use italic text effect.
- [0] An expression resolving to a boolean for the enable state. 0 = off, 1 = on
The expression can be evaluated using ISeStringEvaluator (code).
[0x1B] Edge
Unknown purpose.
[0x1C] Shadow
Unknown purpose.
[0x1D] NonBreakingSpace
Adds a non-breaking space.
No expressions.
Macro string: <nbsp>
→ Prints (\u00A0).
[0x1E] Icon2
Behaves like the icon macro, but dynamically remaps controller
button icons based on the player's configured Button Configuration.
[0x1F] Hyphen
Adds a hyphen.
No expressions.
Macro string: <-->
→ Prints -.
[0x20] Num
Adds a decimal representation of an integer expression.
Expressions:
- [0] Integer Expression: Value
Can be evaluated using ISeStringEvaluator (code).
Example
It's currently hour <num(gnum11)>.
→ Prints It's currently hour 5. if gnum11 (hour of current Eorzea Time)
is 5.
var example = new SeStringBuilder()
.Append("It's currently hour ")
.BeginMacro(MacroCode.Num)
.AppendGlobalNumberExpression(11)
.EndMacro()
.Append(".")
.ToReadOnlySeString();
var result = SeStringEvaluator.Evaluate(example);
[0x21] Hex
Adds a hexadecimal representation of an integer expression.
Expressions:
- [0] Integer Expression: Value
Can be evaluated using ISeStringEvaluator (code).
Example
15 in hexadecimal is <hex(15)>.
→ Prints 15 in hexadecimal is 0x0000000F.
var example = new SeStringBuilder()
.Append("15 in hexadecimal is ")
.BeginMacro(MacroCode.Hex)
.AppendIntExpression(15)
.EndMacro()
.Append(".")
.ToReadOnlySeString();
var result = SeStringEvaluator.Evaluate(example);
[0x22] Kilo
Adds a decimal representation of an integer expression, separating by thousands.
Expressions:
- [0] Integer Expression: Value
- [1] String Expression: Separator (usually a comma or a dot)
Can be evaluated using ISeStringEvaluator (code).
Example
The damage was over <kilo(9000,.)>.
→ Prints The damage was over 9.000.
var example = new SeStringBuilder()
.Append("The damage was over ")
.BeginMacro(MacroCode.Kilo)
.AppendIntExpression(9000)
.AppendStringExpression(".")
.EndMacro()
.Append(".")
.ToReadOnlySeString();
var result = SeStringEvaluator.Evaluate(example);
[0x23] Byte
Adds a human-readable byte string (possible suffixes: omitted, K, M, G, T).
Expressions:
- [0] Integer Expression: Value
ISeStringEvaluator does currently not support evaluation for this macro.
Example
The file size is <byte(150000)>.
→ Prints The file size is 146.5K.
var example = new SeStringBuilder()
.Append("The file size is")
.BeginMacro(MacroCode.Byte)
.AppendIntExpression(150000)
.EndMacro()
.Append(".")
.ToReadOnlySeString();
[0x24] Sec
Adds a zero-padded-to-two-digits decimal representation of an integer expression.
Expressions:
- [0] Integer Expression: Value
Can be evaluated using ISeStringEvaluator (code).
Example
The current time is <sec(gnum11)>:<sec(gnum12)>.
→ Prints The current time is 04:32. when the Eorzea Time is 04:32.
var example = new SeStringBuilder()
.Append("The current time is ")
.BeginMacro(MacroCode.Sec)
.AppendGlobalNumberExpression(11)
.EndMacro()
.Append(":")
.BeginMacro(MacroCode.Sec)
.AppendGlobalNumberExpression(12)
.EndMacro()
.Append(".")
.ToReadOnlySeString();
var result = SeStringEvaluator.Evaluate(example);
[0x25] Time
Unknown purpose.
[0x26] Float
Adds a floating point number as text.
Expressions:
- [0] Integer Expression: Value
- [1] Integer Expression: Radix
- [2] String Expression: Separator
Can be evaluated using ISeStringEvaluator (code).
Example
The limit break is filled up to <float(1337,100,.)> %.
→ Prints The limit break is filled up to 13.37 %.
var example = new SeStringBuilder()
.Append("The limit break is filled up to ")
.BeginMacro(MacroCode.Float)
.AppendIntExpression(1337)
.AppendIntExpression(100)
.AppendStringExpression(".")
.EndMacro()
.Append(" %.")
.ToReadOnlySeString();
var result = SeStringEvaluator.Evaluate(example);
[0x27] Link
Begins or ends a region of link.
Expressions:
- [0] Integer Expression: LinkMacroPayloadType
- [1] Integer Expression: Usage depends on LinkMacroPayloadType, most of the time it's an Id
- [2] Integer Expression: Usage depends on LinkMacroPayloadType
- [3] Integer Expression: Usage depends on LinkMacroPayloadType
- [4] String Expression: Plain string of the linked thing, used when the text is copied to the clipboard
Always make sure that a link payload has a corresponding link terminator payload.
This does not add formatting or the link marker to the output.
To add the link marker you can evaluate Addon#371 with the link as local parameter.
For some link types you can also use the fixed macro instead,
which adds proper formatting too (for example, the item name rarity color).
Example
<link(2,4801,0,0,Dalamud Nut)>Dalamud Nut<link(0xCE,0,0,0)>
→ Prints a clickable Dalamud Nut item link.
[0x28] Sheet
Adds a column from a sheet.
Expressions:
- [0] String Expression: Sheet Name
- [1] Integer Expression: RowId
- [2] Integer Expression: Column Index
- [3] Expression used as local parameter to evaluate the the columns text
Can be evaluated using ISeStringEvaluator (code).
Example
<sheet(Addon,762,0,3)>, with Addon#762 being <sheet(Town,lnum1,0)>
→ Prints Ul'dah
var example = new SeStringBuilder()
.BeginMacro(MacroCode.Sheet)
.AppendStringExpression("Addon")
.AppendIntExpression(762)
.AppendIntExpression(0)
.AppendIntExpression(3)
.EndMacro()
.ToReadOnlySeString();
var result = SeStringEvaluator.Evaluate(example);
[0x29] String
Adds a string expression as-is. Used for evaluation purposes (like filling in placeholders).
Expressions:
- [0] String Expression: Text
Can be evaluated using ISeStringEvaluator (code).
Example
This is <string(lstr1)>!
→ Prints This is amazing! when lstr1 is amazing.
var example = new SeStringBuilder()
.Append("This is ")
.BeginMacro(MacroCode.String)
.AppendLocalStringExpression(1)
.EndMacro()
.Append("!")
.ToReadOnlySeString();
var result = SeStringEvaluator.Evaluate(example, ["amazing"]);
[0x2A] Caps
Adds a string, fully upper cased.
Expressions:
- [0] String Expression: Text
Can be evaluated using ISeStringEvaluator (code).
Example
This is <caps(lstr1)>!
→ Prints This is AMAZING! when lstr1 is amazing.
var example = new SeStringBuilder()
.Append("This is ")
.BeginMacro(MacroCode.Caps)
.AppendLocalStringExpression(1)
.EndMacro()
.Append("!")
.ToReadOnlySeString();
var result = SeStringEvaluator.Evaluate(example, ["amazing"]);
[0x2B] Head
Adds a string, first character upper cased.
Expressions:
- [0] String Expression: Text
Can be evaluated using ISeStringEvaluator (code).
Example
<head(<sheet(ContentFinderCondition,22,43)>)> where ContentFinderCondition
RowId 22, Column 43 is the Lost City of Amdapor
→ Prints The Lost City of Amdapor.
var example = new SeStringBuilder()
.BeginMacro(MacroCode.Head)
.BeginStringExpression()
.BeginMacro(MacroCode.Sheet)
.AppendStringExpression("ContentFinderCondition")
.AppendIntExpression(22)
.AppendIntExpression(43)
.EndMacro()
.EndExpression()
.EndMacro()
.ToReadOnlySeString();
var result = SeStringEvaluator.Evaluate(example, default, ClientLanguage.English);
[0x2C] Split
Splits the input string by a given separator and returns the element at the specified position.
Expressions:
- [0] String Expression: Text
- [1] String Expression: Separator
- [2] Integer Expression: Index, starting at 1
Can be evaluated using ISeStringEvaluator (code).
Example
<split(Forename Lastname, ,2)>
→ Prints Lastname.
var example = new SeStringBuilder()
.BeginMacro(MacroCode.Split)
.AppendStringExpression("Firstname Lastname")
.AppendStringExpression(" ")
.AppendIntExpression(2)
.EndMacro()
.ToReadOnlySeString();
var result = SeStringEvaluator.Evaluate(example);
[0x2D] HeadAll
Adds a string, every words first character upper cased.
Expressions:
- [0] String Expression: Text
Can be evaluated using ISeStringEvaluator (code).
Example
<headall(the great gubal library)>
→ Prints The Great Gubal Library.
var example = new SeStringBuilder()
.BeginMacro(MacroCode.HeadAll)
.AppendStringExpression("the great gubal library")
.EndMacro()
.ToReadOnlySeString();
var result = SeStringEvaluator.Evaluate(example);
[0x2E] Fixed
A multi-functional macro to generate auto translated links or texts.
Can be evaluated using ISeStringEvaluator (code).
Usages:
Auto Translation
If the first expression is neither 100 nor 200, the fixed macro is used for the auto-translation system.
Expressions:
- [0] Integer Expression: Group column in the Completion sheet (0-indexed in the macro)
- [1] Integer Expression: RowId of the referenced sheet (depends on the LookupTable column - if empty, uses Completion sheet)
<fixed(0,101)>
→ Prints
Please use the auto-translate function.Based on the LookupTable for Group 49, the RowId is for the Mount sheet:
<fixed(48,209)>
→ Prints
albino karakulThe following uses all have 200 as the first expression (100 would also work and is identical to 200). We can only assume that these numbers indicate the version of the game (1.00 for FFXIV, 2.00 for FFXIV ARR).
[1] Player Link
If the second expression is 1, the fixed macro generates a player link.
Expressions:
- [0] Integer Expression: 200
- [1] Integer Expression: 1
- [2] Integer Expression: World Id
- [3] String Expression: Player Name
<fixed(200,1,1,Player Name)>
→ Prints interactable player link Player NameDev
if the World Id is not the owns Home World Id.
→ Prints interactable player link Player Name if the World Id is the owns Home
World Id.
[2] ClassJob Level
If the second expression is 2, the fixed macro prints the ClassJob name and level.
Expressions:
- [0] Integer Expression: 200
- [1] Integer Expression: 2
- [2] Integer Expression: ClassJob Id
- [3] Integer Expression: Level
<fixed(200,2,28,0)>
→ Prints scholar.
<fixed(200,2,28,100)>
→ Prints scholar(100).
[3] Map Link
If the second expression is 3, the fixed macro generates a map link.
Expressions:
- [0] Integer Expression: 200
- [1] Integer Expression: 3
- [2] Integer Expression: TerritoryType Id
- [3] Integer Expression: Packed Ids
- Instance (upper 16 bits as ushort):
value >> 16 - Map Id (lower 16 bits as ushort):
value & 0xFFFF
- Instance (upper 16 bits as ushort):
- [4] Integer Expression: Raw X coordinates
- [5] Integer Expression: Raw Y coordinates
- [6] Integer Expression: Raw Z coordinates (if not available use 0xFFFF8AD0)
- [7] Integer Expression: PlaceName Id override (if not 0, otherwise defaulted to the TerritoryType's PlaceName)
<fixed(200,3,146,23,0xFFFE896A,0xFFFD0649,0xFFFF8AD0,0)>
→ Prints interactable map link Southern Thanalan ( 19.5 ,
17.5 ).
[4] Item Link
If the second expression is 4, the fixed macro generates an item link.
Expressions:
- [0] Integer Expression: 200
- [1] Integer Expression: 4
- [2] Integer Expression: Item Id with flags applied or EventItem Id
- [3] Integer Expression: Rarity (for the item name color)
- 1 = White
- 2 = Green
- 3 = Blue
- 4 = Purple (Relics)
- 5 = Orange
- 6 = Yellow
- 7 = Pink (Aetherial Items)
- [4] Integer Expression: Unknown
- [5] Integer Expression: Unknown
- [6] String Expression: Item Name
<fixed(200,4,4801,1,0,0,Dalamud Nut)>
→ Prints interactable item link Dalamud Nut.
[5] Chat Sound Effect
If the second expression is 5, the fixed macro plays a chat sound effect and
prints its <se.#> code.
Expressions:
- [0] Integer Expression: 200
- [1] Integer Expression: 5
- [2] Integer Expression: Sound Effect Id (0-indexed)
<fixed(200,5,5)>
→ Prints <se.6> and plays the bongo sound effect.
To prevent sounds from playing every frame, ISeStringEvaluator will not play
the sound effect. The payload will only be evaluated to a plain string, making
the game also not play the sound effect when printed to chat. Use
UIGlobals.PlayChatSoundEffect()
from ClientStructs if you want to play it.
[6] ObjStr name
If the second expression is 6, the fixed macro prints an ObjStr's name.
Expressions:
- [0] Integer Expression: 200
- [1] Integer Expression: 6
- [2] Integer Expression: ObjStr Id (see ObjectKind.GetObjStrId)
<fixed(200,6,1008170)>
→ Prints Cid, based on ENpcResident 1008170.
[7] String
If the second expression is 7, the fixed macro prints the string that was passed to it.
Expressions:
- [0] Integer Expression: 200
- [1] Integer Expression: 6
- [2] String Expression
<fixed(200,7,Hello World!)>
→ Prints Hello World!.
[8] Time Remaining
If the second expression is 8, the fixed macro prints the remaining time in a formatted style.
Expressions:
- [0] Integer Expression: 200
- [1] Integer Expression: 6
- [2] Integer Expression: Remaining time in seconds
<fixed(200,8,69)>
→ Prints 1:09.
[9] Unknown
It's currently unclear what type 9 does, but it may be related to the Mentor or Beginner icons that appear in front of player names in the Novice Network chat channel.
[10] Status Link
If the second expression is 10, the fixed macro generates a status link.
Expressions:
- [0] Integer Expression: 200
- [1] Integer Expression: 10
- [2] Integer Expression: Status Id
- [3] Boolean Expression: Has Override
- [4] String Expression: Status Name Override (optional, depending on Has Override)
- [5] String Expression: Status Description Override (optional, depending on Has Override)
<fixed(200,10,851,0)>
→ Prints interactable status link Reassembled.
<fixed(200,10,3698,0)>
→ Prints interactable status link Forward
March.
[11] Party Finder Link
If the second expression is 11, the fixed macro generates a party finder link.
Expressions:
- [0] Integer Expression: 200
- [1] Integer Expression: 11
- [2] Integer Expression: Listing Id
- [3] Integer Expression: Unknown
- [4] Integer Expression: World Id
- [5] Integer Expression: Cross World flag (0 = Cross World, 1 = not Cross World)
- [6] String Expression: Player Name
<fixed(200,11,123456,1,1,0,Player Name)>
→ Prints interactable party finder link Looking for Party
(Player Name) .
[12] Quest Link
If the second expression is 12, the fixed macro generates a quest link.
Expressions:
- [0] Integer Expression: 200
- [1] Integer Expression: 12
- [2] Integer Expression: Quest Id
- [3] Integer Expression: Unused
- [4] Integer Expression: Unused
- [5] Integer Expression: Unused
- [6] String Expression: Quest Name
<fixed(200,12,70058,0,0,0,The Ultimate Weapon)>
→ Prints interactable quest link The Ultimate Weapon.
[0x2F] Lower
Adds a string, fully lower cased.
Expressions:
- [0] String Expression: Text
Can be evaluated using ISeStringEvaluator (code).
Example
<lower(CHOCOBO)>
→ Prints chocobo.
var example = new SeStringBuilder()
.BeginMacro(MacroCode.Lower)
.AppendStringExpression("CHOCOBO")
.EndMacro()
.ToReadOnlySeString();
var result = SeStringEvaluator.Evaluate(example);
[0x30] JaNoun
Adds a properly formatted name based on the games noun system for the Japanese language.
Expressions:
- [0] String Expression: Sheet Name
- [1] Integer Expression: JapaneseArticleType
- [2] Integer Expression: RowId
- [3] Integer Expression: Amount
Can be evaluated using ISeStringEvaluator (code, NounProcessor).
For examples, see the Noun Processor widget in /xldata.
[0x31] EnNoun
Adds a properly formatted name based on the games noun system for the English language.
Expressions:
- [0] String Expression: Sheet Name
- [1] Integer Expression: EnglishArticleType
- [2] Integer Expression: RowId
- [3] Integer Expression: Amount
Can be evaluated using ISeStringEvaluator (code, NounProcessor).
For examples, see the Noun Processor widget in /xldata.
[0x32] DeNoun
Adds a properly formatted name based on the games noun system for the German language.
Expressions:
- [0] String Expression: Sheet Name
- [1] Integer Expression: GermanArticleType
- [2] Integer Expression: RowId
- [3] Integer Expression: Amount
- [4] Integer Expression: Grammatical Case
- 1 = Nominative
- 2 = Genitive
- 3 = Dative
- 4 = Accusative
Can be evaluated using ISeStringEvaluator (code, NounProcessor).
For examples, see the Noun Processor widget in /xldata.
[0x33] FrNoun
Adds a properly formatted name based on the games noun system for the French language.
Expressions:
- [0] String Expression: Sheet Name
- [1] Integer Expression: FrenchArticleType
- [2] Integer Expression: RowId
- [3] Integer Expression: Amount
Can be evaluated using ISeStringEvaluator (code, NounProcessor).
For examples, see the Noun Processor widget in /xldata.
[0x34] ChNoun
Not supported in Dalamud.
[0x40] LowerHead
Adds a string, first character lower cased.
Expressions:
- [0] String Expression: Text
Can be evaluated using ISeStringEvaluator (code).
Example
<lowerhead(CHOCOBO)>
→ Prints cHOCOBO.
var example = new SeStringBuilder()
.BeginMacro(MacroCode.LowerHead)
.AppendStringExpression("CHOCOBO")
.EndMacro()
.ToReadOnlySeString();
var result = SeStringEvaluator.Evaluate(example);
[0x41] SheetSub
Adds a string from a subsheets secondary sheet.
Expressions:
- [0] String Expression: Sheet Name
- [1] Integer Expression: RowId
- [2] Integer Expression: SubrowId
- [3] Integer Expression: Column Index
- [4] String Expression: Secondary Sheet Name
- [5] String Expression: Secondary Sheet Column Index
Example
<sheetsub(WKSPioneeringTrail,1,1,3,WKSPioneeringTrailString,1)>
→ Prints Peaceful Living and Technological Leaps.
var example = new SeStringBuilder()
.BeginMacro(MacroCode.SheetSub)
.AppendStringExpression("WKSPioneeringTrail")
.AppendIntExpression(1)
.AppendIntExpression(3)
.AppendIntExpression(3)
.AppendStringExpression("WKSPioneeringTrailString")
.AppendIntExpression(1)
.EndMacro()
.ToReadOnlySeString();
[0x42] SwitchPlatform
Prints text from the Platform sheet, depending on the current clients' platform.
Expressions:
- [0] Integer Expression: Text Index
Can be evaluated using ISeStringEvaluator (code).
The Platform sheet is split into two sections: the first 20 rows are for wired controllers, and the next 20 rows are for wireless controllers.
On Windows, however, it currently always prints Gamepad for any text index
that’s passed in.
We assume the original code contains platform-specific C preprocessor sections that were omitted from the Windows build.
Example
<switchplatform(1)>
→ Prints Gamepad.
var example = new SeStringBuilder()
.BeginMacro(MacroCode.SwitchPlatform)
.AppendUIntExpression(1)
.EndMacro()
.ToReadOnlySeString();
var result = SeStringEvaluator.Evaluate(example);
→ Prints Gamepad.
[0x48] ColorType
Pushes the text foreground color, referring to a color defined in UIColor sheet.
Expressions:
- [0] Integer Expression: RowId of UIColor sheet
Expression can be evaluated using ISeStringEvaluator (code).
Always make sure that when you push a colortype, it is popped from the stack
with stackcolor using the color macro!
[0x49] EdgeColorType
Pushes the text border color, referring to a color defined in UIColor sheet.
Expressions:
- [0] Integer Expression: RowId of UIColor sheet
Expression can be evaluated using ISeStringEvaluator (code).
Always make sure that when you push an edgecolortype, it is popped from the
stack with stackcolor using the edgecolor macro!
[0x4A] Ruby
Displays ruby text (furigana, interlinear annotation) above standard text.
Expressions:
- [0] String Expression: Standard text
- [1] String Expression: Ruby text
Presumably only supported in cutscene dialogs.
[0x50] Digit
Adds a zero-padded number as text.
Expressions:
- [0] Integer Expression: Value
- [1] Integer Expression: Target length
Can be evaluated using ISeStringEvaluator (code).
Example
<digit(15,4)>
→ Prints 0015.
var example = new SeStringBuilder()
.BeginMacro(MacroCode.Digit)
.AppendIntExpression(15)
.AppendIntExpression(4)
.EndMacro()
.ToReadOnlySeString();
var result = SeStringEvaluator.Evaluate(example);
[0x51] Ordinal
Adds an ordinal number as text (English only).
Expressions:
- [0] Integer Expression: Value
Can be evaluated using ISeStringEvaluator (code).
Example
<ordinal(1)> <ordinal(2)> <ordinal(3)> <ordinal(4)>
→ Prints 1st 2nd 3rd 4th.
var example = new SeStringBuilder()
.BeginMacro(MacroCode.Ordinal)
.AppendIntExpression(1)
.EndMacro()
.Append(" ")
.BeginMacro(MacroCode.Ordinal)
.AppendIntExpression(2)
.EndMacro()
.Append(" ")
.BeginMacro(MacroCode.Ordinal)
.AppendIntExpression(3)
.EndMacro()
.Append(" ")
.BeginMacro(MacroCode.Ordinal)
.AppendIntExpression(4)
.EndMacro()
.ToReadOnlySeString();
var result = SeStringEvaluator.Evaluate(example);
[0x60] Sound
Adds an invisible sound payload.
Expressions:
- [0] Integer Expression: Bool whether this sound is part of the Jingle sheet
- [1] Integer Expression: Sound Id
[0x61] LevelPos
Adds a formatted map name and corresponding coordinates.
Expressions:
- [0] Integer Expression: RowId in Level sheet
Can be evaluated using ISeStringEvaluator (code).
Example
<levelpos(3871103)>
→ Prints
South Shroud
( 27.7 , 21.1 )
var example = new SeStringBuilder()
.BeginMacro(MacroCode.LevelPos)
.AppendIntExpression(3871103)
.EndMacro()
.ToReadOnlySeString();
var result = SeStringEvaluator.Evaluate(example);
Evaluating SeStrings
In order to evaluate payloads use the ISeStringEvaluator service.
Let's reuse our placeholder expression example from before, but this time using a local parameter:
var template = ReadOnlySeString.FromMacroString("The current time is: <settime(lnum1)><num(t_hour)>:<num(t_min)>");
var example = SeStringEvaluator.Evaluate(template, [1743880207]);
The payloads of the template variable are looped over, will be evaluated and
the resulting plain text is added to an internal SeStringBuilder, resulting in a
new ReadOnlySeString. Since all payloads in the example above are evaluated, the
example variable will now only contain the text The current time is: 21:10.
The following macro codes are always passed through:
- Hyphen
- Icon
- Icon2
- Link
- NewLine
- NonBreakingSpace
- SoftHyphen
- Sound
- Wait
The expressions for the following macro codes are evaluated, but the payloads are passed through because they are used to format text:
- Color
- EdgeColor
- ShadowColor
- Bold
- Italic
- ColorType
- EdgeColorType
The following macro codes are currently not supported by the evaluator and will be passed through:
- Byte
- ChNoun
- Edge
- Josa
- Josaro
- Key
- Ruby
- Scale
- Shadow
- Time
Rendering SeStrings in ImGui
If you're certain a ReadOnlySeString doesn't contain macro payloads, you can
safely convert it to a plain C# string using ToString(). This function strips
out all macro payloads except for NewLine, NonBreakingSpace and Hyphen, which
are replaced with their corresponding UTF-8 characters.
If you do want to preserve and render formatting payloads, Dalamud provides convenient SeString rendering helpers for ImGui. These handle soft hyphens and formatting properly, so you don’t have to deal with the quirks yourself:
ImGuiHelpers.SeStringWrapped()forReadOnlySeStringorReadOnlySeStringSpan,ImGuiHelpers.CompileSeStringWrapped()for macro strings.